How to regulate your digestion from within?
Problems with going to the bathroom, feeling bloated, abdominal cramps or heartburn are, in many cases, symptoms of digestive enzymes deficiency. The gastrointestinal system produces and secretes enzymes that participate in the breakdown of nutrients into smaller, simpler molecules during their transit through the digestive system. Upon reaching the small intestine, these digested nutrients will be able to pass through the intestinal villi and enter the bloodstream. Once in the blood, they will be transported to the cells, where they will be used to obtain energy for cell growth and repair ,or for the synthesis of the substances necessary for the regulation of metabolic processes.
Examples of digestive enzymes are carbohydrate-digesting amylases, fat-digesting lipases, and protein-digesting proteases.
For everything in our body to function properly, from hormones to the heart, the simple nutrients resulting from the digestive process are essential.
The decrease in the production of digestive enzymes with age
When we are young, our body creates all the enzymes necessary for a healthy and complete digestion. But as we age, this production begins to decline1,2.The deficit of digestive enzymes affects the absorption and use of nutrients, and increases the amount of partially digested nutrients in the digestive tract. These nutrients will be fully exposed and available to the bacteria in the intestine, which will cause the production of gases by fermentation, generating discomfort, such as abdominal bloating, constipation and flatulence. The origin of this enzymatic decline is related to the aging of important organs, such as the liver and pancreas. Both the size of the liver and the blood flow to the liver have been observed to decrease with age.
At the level of the pancreas, a negative correlation between age and pancreatic size has also been observed3 .In some diseases, such as chronic pancreatitis, the body produces insufficient amounts of digestive enzymes necessary for the breakdown of food, and patients with this disease often suffer from malnutrition.
Lactose intolerance
Another common example of digestive problems, derived from enzyme deficiency, is intolerance to lactose, a sugar present in milk. Around 75% of the world’s population has problems digesting dairy products4, due to a deficit in the production of the lactase (β-galactosidase) enzyme in the small intestine. Without lactase, the body is not able to digest lactose. As a result, lactose will reach the intestine intact and will serve as food for the intestinal bacteria, which will involve the formation of gases by fermentation, producing flatulence, pain and abdominal bloating.
Digestive enzymes in the fight against functional dyspepsia and other intestinal problems
The term “dyspepsia”, popularly referred to as heavy digestion, is used to describe any type of digestive discomfort such as abdominal pain, gastroesophageal reflux, unpleasant taste from the mouth, heartburn, the feeling of abdominal bloating, the production of belching, flatulence, and rumbling (bowel sounds) 5,6.
“Functional dyspepsia” is not related to organic (gastritis, reflux esophagitis), infectious (Helicobacter pylori infection), metabolic (hypothyroidism, acidosis) or drug-induced disorders. It has its origin in an abnormal perception of the patient, or in an alteration of the function of the upper digestive tract 7. One of the main causes of functional dyspepsia is age. As we have commented previously, the natural aging of some organs results in a decrease in the production of digestive enzymes, which will affect the quality of digestion. However, this digestive disorder is not exclusive to older people. The younger population also tends to present symptoms of functional dyspepsia, usually induced by behavioral and psychic factors, such as 7,8 :
- Adoption of a diet low in fiber and rich in processed foods.
- Poor chewing of food due to hasty eating habits.
- Disorder in meal times.
- High caffeine consumption.
- Anxiety and frequent stress. The mental state produces motor, blood flow and secretory alterations in the digestive system, which affect digestion.
- Lack of physical exercise and obesity. The lack of healthy abdominal muscles and excess weight, result in a weak abdominal muscular wall, contributing to the slowdown of gastrointestinal motility.
- Smoking, alcohol, and excessive use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, naproxen, or diclofenac).
Classical therapeutic intervention includes the use of antacids, prokinetics, histamine H2 receptor antagonists, proton pump inhibitors, and antidepressants 8,9. In less severe cases, digestive enzyme therapy has been studied as a viable and safer alternative. In fact, some studies suggest that the consumption of multienzyme preparations such as DIGELIT, is beneficial in reducing the symptoms of flatulence, abdominal bloating, belching and postprandial heaviness 10,13.
The first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a multienzyme complex for the control of the symptoms of functional dyspepsia, was carried out in 2018 with the enzyme complex DigeZyme®, present in the DIGELIT formula12. DigeZyme® is a combination of five digestive enzymes (amylase, protease, cellulase, lactase, and lipase) that help break down carbohydrates, complex proteins, cellulosic fibers, lactose, and fats. In this study participated 40 patients with functional dyspepsia. They were divided into two equal groups. One group received a 150 mg supplement of the DigeZyme® complex, divided into 3 capsules of 50 mg each. The second group received 3 capsules with placebo. All patients were allowed to continue maintain their normal diet, without any change in their daily routines. Comparisons between the two groups revealed that individuals who received DigeZyme® enzyme complex supplementation had a significant reduction (p <0.01, 99% confidence level) in symptoms of epigastric pain, postprandial bloating, indigestion, heartburn and nausea with no adverse effects. Improvements in functional dyspepsia symptoms were observed at the end of 30 days of supplementation and remained the same until the end of the study (day 60).
Each recommended dose of DIGELIT contains 200 mg of the enzyme complex DigeZyme®, an amount greater than that used in this study, which guarantees the effectiveness of its formula.
Bromelain is a general name for a group of proteases or proteolytic enzymes, found in the Bromeliaceae family plants, of which pineapple (Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.) is the most known. Due to its proteolytic activity (ability to break down proteins) and its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory power, bromelain is ideal for the control of functional dyspepsia 5, 14.
In 1970 was published the first scientific work, in which the efficacy of the combination of bromelain with other digestive enzymes (trypsin, lipase and amylase) was recognized in patients with chronic pancreatic insufficiency.15 Bromelain shows maximum proteolytic activity in a wide pH range, between pH 3 and pH 8 (from acidic to alkaline)15, which makes it a very versatile and active enzyme, both in the stomach and in the small intestine. 16 In fact, in vitro studies have shown that its effect on the digestion of casein at pH 3.3 is similar to that of pepsin and, at pH 6, it is similar to that of trypsin15.
It is important to note the antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties of bromelain. Studies with animal models have shown that bromelain acts against severe diarrhea caused by intestinal infections, caused by pathogens such as Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli, by preventing the adhesion and colonization of these pathogens on the internal walls of the intestine17.
Following a medical report published in 2000, where a reduction in the symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease or IBS (Inflammatory Bowel Disease) was seen in patients who had supplemented their diet with bromelain bromelina 18, Scientists from the Durham Medical Center in the United States investigated the ability of this substance to be used against colitis in in vivo studies19. The study confirmed the anti-inflammatory capacity of bromelain in the cells of the colon of the studied animals after only 5 weeks of oral administration.
The digestive properties of fennel, ginger and gentian seed extracts
Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Mill.) is a plant native to Mediterranean Europe. In Spain it can be found in almost the entire territory, being frequently noticed by the sides of the roads, in cultivated fields and bushes, from sea level and up to 1200 meters of altitude 20. Fennel seeds are traditionally used for their carminative properties in the symptomatic treatment of digestive disorders, such as flatulence, constipation and abdominal bloating 21-25.
The active substance responsible for these properties is anethole, a phenolic ether that is the main component of fennel seeds. Anethole has a structural similarity to catecholamines such as dopamine and competes for the same receptors, blocking their access to the entry of dopamine 24,26. This is exactly the mechanism of action of domperidone, a selective dopamine receptor blocking drug used to treat functional digestive disorders, accelerate gastric and intestinal emptying, and treat nausea and vomiting 27.
Gentian roots (Gentiana lutea L.) have a bitter taste, due to the presence of secoiridoid glycosides that confer beneficial properties on the digestive system, by making the digestion lighter, stimulating appetite, and helping the expulsion and hepatic secretion of bile retained in the gallbladder 28, 29. In addition to treating poor appetite, gentian root can help treat an upset stomach, nausea and gas 28, 30.
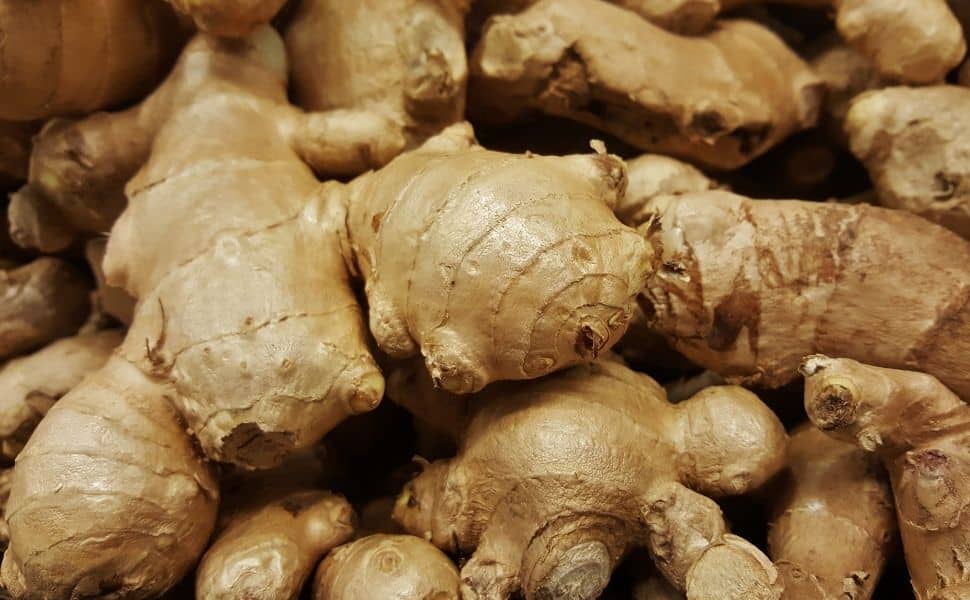
Ginger root (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) has carminative properties, reduces pressure on the lower esophageal sphincter, reduces intestinal cramps and prevents dyspepsia, flatulence and abdominal bloating31-33. The use of ginger helps digestive processes, both in people with functional dyspepsia 34 and in healthy individuals 35 without side effects, which shows its use both in treatment and prevention of digestive problems. Ginger root has a variety of bioactive phytochemical compounds, such as gingerols, shogaols, zingiberenes, which can stimulate oral and gastric secretions and normalize gastrointestinal motility. These compounds can communicate with the 5HT3 and NK1 (neurokinin 1) receptors, which participate in the transfer of information between the gastrointestinal tract and the enteric nervous system, regulating intestinal motility and peristalsis36. This mechanism of action is also used by antiemetic drugs, such as rolapitant or aprepitant, used to prevent or control postoperative nausea and vomiting.
The enteric nervous system (ENS) is a subdivision of the autonomic nervous system that is in charge to directly control the digestive system, warn of hunger and satiety and to prevent invasive and harmful substances from entering the body.
In short, supplementing the diet with digestive enzymes and plant extracts with digestive properties can provide greater digestive comfort to people with functional dyspepsia, both due to an enzyme deficit and induced by behavioral and psychological factors. For this purpose, Nutribiolite has developed DIGELIT, a food supplement that combines digestive enzymes and selected plant extracts, which work together to aid in the digestive process. Its formula combines bromelain (a natural enzyme from pineapple), with the patented DigeZyme® multi-enzyme complex, both with high enzyme activity. Digestive enzymes assist in the breakdown of food into simpler nutrients, reducing their time spent in the intestine. As a consequence, the probability of occurrence of episodes of constipation and the production of intestinal gases that generate flatulence, pain and abdominal bloating decreases. The selected extracts of fennel, gentian and ginger, help to stimulate gastric secretions, to normalize gastrointestinal motility, favoring the emptying of the intestine. 25, 29, 33 Bromelain also has important antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, which can help prevent colonization of pathogens on the inner walls of the intestine.
- Morley, J.E., The aging gut: physiology. Clin Geriatr Med, 2007. 23(4): p. 757-67, v-vi.
- Laugier, R., et al., Changes in pancreatic exocrine secretion with age: pancreatic exocrine secretion does decrease in the elderly. Digestion, 1991. 50(3-4): p. 202-11.
- Löhr, J.M., et al., The ageing pancreas: a systematic review of the evidence and analysis of the consequences. J Intern Med, 2018. 283(5): p. 446-460.
- Silanikove, N., G. Leitner, and U. Merin, The Interrelationships between Lactose Intolerance and the Modern Dairy Industry: Global Perspectives in Evolutional and Historical Backgrounds. Nutrients, 2015. 7(9): p. 7312-7331.
- Martín-Aragón, S., Dispepsia funcional. Farmacia Profesional, 2006. 20(10): p. 50-55.
- Chua, A.S.B., Reassessment of functional dyspepsia: a topic review. World journal of gastroenterology, 2006. 12(17): p. 2656-2659.
- Sebastián Domingo, J.J., Dispepsia funcional.Descripción y tratamiento. Farmacia Profesional, 2002. 16(5): p. 58-64.
- Corsetti, M. and M. Fox, The management of functional dyspepsia in clinical practice: what lessons can be learnt from recent literature? [version 1; peer review: 2 approved]. F1000Research, 2017. 6(1778).
- Chen, S.L., A review of drug therapy for functional dyspepsia. J Dig Dis, 2013. 14(12): p. 623-5.
- Pawar, D., Efficacy And Tolerability Of Unienzyme – Mps – A Multienzyme Preparation With Simethicone In Patients With Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia. Indian medical gazette, 2001: p. 294-305.
- Khandke, D.A. and S. Jain. Post-Marketing Surveillance Study to Assess the Efficacy and Tolerability of Al 5 zyme@ A Multienzyme Preparation in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia. 2013.
- Majeed, M., et al., Evaluation of the Safety and Efficacy of a Multienzyme Complex in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. J Med Food, 2018. 21(11): p. 1120-1128.
- Suarez, F., et al., Pancreatic supplements reduce symptomatic response of healthy subjects to a high fat meal. Dig Dis Sci, 1999. 44(7): p. 1317-21.
- Chakraborty, A.J., et al., Bromelain a Potential Bioactive Compound: A Comprehensive Overview from a Pharmacological Perspective. Life, 2021. 11(4): p. 317.
- Knill-Jones, R.P., et al., Comparative trial of Nutrizym in chronic pancreatic insufficiency. British medical journal, 1970. 4(5726): p. 21-24.
- Yoshioka, S., et al., Inactivation kinetics of enzyme pharmaceuticals in aqueous solution. Pharm Res, 1991. 8(4): p. 480-4.
- Mynott, T.L., et al., Bromelain prevents secretion caused by Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli enterotoxins in rabbit ileum in vitro. Gastroenterology, 1997. 113(1): p. 175-84.
- Use of Bromelain for Mild Ulcerative Colitis. Annals of Internal Medicine, 2000. 132(8): p. 680.
- Hale, L.P., et al., Treatment with oral bromelain decreases colonic inflammation in the IL-10-deficient murine model of inflammatory bowel disease. Clinical Immunology, 2005. 116(2): p. 135-142.
- S., C., Flora iberica: plantas vasculares de la Península Ibérica e Islas Baleares. Araliaceae-Umbillifeare. Vol. Vol. XX. 2013, Madrid: Real Jardín Botánico-CSIC.
- Badgujar, S.B., V.V. Patel, and A.H. Bandivdekar, Foeniculum vulgare Mill: a review of its botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, contemporary application, and toxicology. Biomed Res Int, 2014. 2014: p. 842674.
- Rather, D.M., et al., Foeniculum vulgare: A comprehensive review of its traditional use, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and safety. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2012. 14.
- Portincasa, P., et al., Irritable bowel syndrome and diet. Gastroenterology report, 2017. 5(1): p. 11-19.
- Asano, T., et al., Anethole restores delayed gastric emptying and impaired gastric accommodation in rodents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2016. 472(1): p. 125-30.
- Extracted from the EFSA health claims application list, under evaluation: ID 2692 – Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) – Spasmolytic and carminative effect.
- Marinov, V. and S. Valcheva-Kuzmanova, Review on the pharmacological activities of anethole. 2015, 2015. 2(2).
- Barone, J.A., Domperidone: a peripherally acting dopamine2-receptor antagonist. Ann Pharmacother, 1999. 33(4): p. 429-40.
- Mirzaee, F., et al., Medicinal, biological and phytochemical properties of Gentiana species. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, 2017. 7(4): p. 400-408.
- Extracted from the EFSA health claims application list, under evaluation: ID 3765 – Gentiana lutea – common name : Gentian – Digestion.
- Assessment report on Gentiana lutea L., radix – Based on Article 16d(1), Article 16f and Article 16h of Directive 2001/83/EC (traditional use).
- Ali, B.H., et al., Some phytochemical, pharmacological and toxicological properties of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe): A review of recent research. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2008. 46(2): p. 409-420.
- Nikkhah Bodagh, M., I. Maleki, and A. Hekmatdoost, Ginger in gastrointestinal disorders: A systematic review of clinical trials. Food science & nutrition, 2018. 7(1): p. 96-108.
- Extracted from the EFSA health claims application list, under evaluation: ID 2172 – Zingiber officinale (Common Name : Ginger) – Digestive health.
- Hu, M.-L., et al., Effect of ginger on gastric motility and symptoms of functional dyspepsia. World journal of gastroenterology, 2011. 17(1): p. 105-110.
- Wu, K.L., et al., Effects of ginger on gastric emptying and motility in healthy humans. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2008. 20(5): p. 436-40.
- Thompson, A.J. and S.C.R. Lummis, 5-HT3 receptors. Current pharmaceutical design, 2006. 12(28): p. 3615-3630.